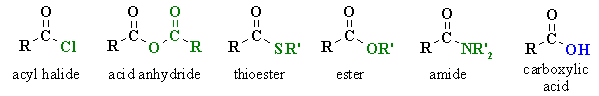 |
Chapter 20: Carboxylic
Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution |
 |
Summary
The carboxylic acid derivatives are
a family of closely related functional groups:
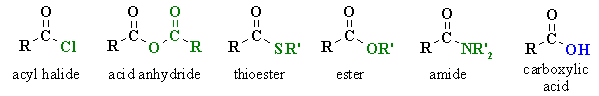
- each contain a C=O group
with a heteroatom attached
(note : this is what distinguishes them from aldehydes
and ketones)
- they can all be prepared from
the "parent" carboxylic acid (review Ch19)
- on hydrolysis (reaction with
H2O) they all convert back to the parent carboxylic acid
- they share a common reactivity
pathway with nucleophiles: nucleophilic acyl substitution.
IMPORTANT
Reactivity order : acyl chloride >
anhydride >
thioester > ester
= carboxylic acid >
amide >
carboxylate
The most important things to know
about carboxylic acid derivatives are:
- how to prepare the derivatives
from the carboxylic acid itself (chapter 19)
- the relative reactivity of the
carboxylic acid derivatives.
- that hydrolysis of derivatives
gets you back to the carboxylic acid.
- the mechanism of nucleophilic
acyl substitution.
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
- Overview
- Summary
of Reactions that Interconvert Carboxylic Acids Derivatives
Reactions of Carboxylic Acid
Derivatives
Spectroscopic Analysis
Problems