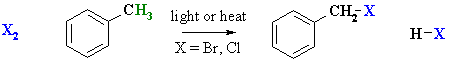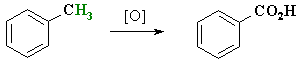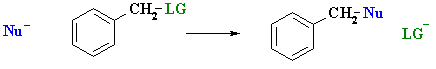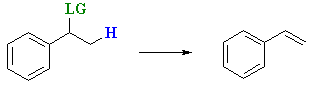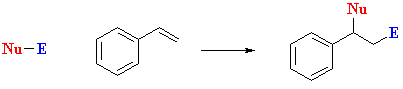|
Chapter 11 : Arenes and Aromaticity |
 |
Reactions of the Benzylic position
Functional groups in a benzylic position are generally more reactive than the
related isolated functional group.
- Benzylic C-H can easily be radically halogenated since the benzylic radical is
resonance stabilised.
- Benzylic C-H bonds of alkyl benzenes can be oxidised
to give benzoic acids
- Benzylic halides readily undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions even with weak nucleophiles.
- Benzylic halides or alcohols readily eliminate to give conjugated alkenes.
- Alkenylbenznes undergo addition reactions to give typical addition products.
These reactions are summarised in the following table: