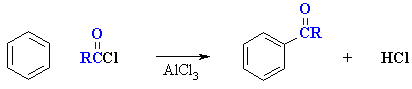 |
Chapter 20: Carboxylic
Acid Derivatives. NucleophilicAcyl Substitution |
 |
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
of Benzene
(review
of Chapter 12)
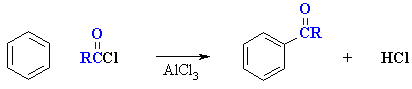
Reaction type: Electrophilic Aromatic
Substitution (of the aromatic),or
Nucleophilic
Acyl Substitution (of the acyl halide)
Summary.
- Overall transformation :
Ar-H to Ar-COR
(aketone)
- Named after Friedel and Crafts
who discovered the reaction.
- Reagent : normally the acyl halide
(e.g. usually RCOCl) with aluminum trichloride, AlCl3,
a Lewis acid catalyst.
- The AlCl3 enhances
the electrophilicity of the acyl halide bycomplexing with the halide.
- Electrophilic species : the acyl
cation or acylium ion (i.e.RCO + ) formed
by the "removal" of the halide by the Lewis acid catalyst.
- Friedel-Crafts reactions are limited
to arenes as or more reactive than mono-halobenzenes.
- Other sources of acylium can also
be used such as acid anhydrides withAlCl3
- Note how the reaction can still
be reviewed as a Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution of the acyl halide
since overall we have a nucleophile (here the π
bond of an aromatic ring) replaces the leaving group (chloride) at the electrophilic
C=O.