| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
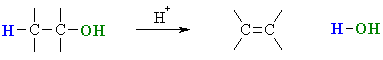
Summary
|
|
|
| Step 1:
An acid/base reaction. Protonation of the alcoholic oxygen to make a better leaving group. This step is very fast and reversible. The lone pairs on the oxygen make it a Lewis base. |
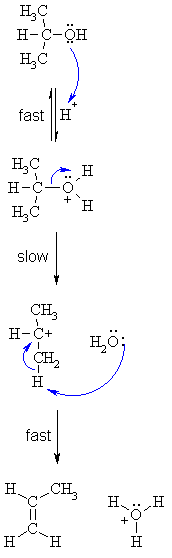 |
| Step 2: Cleavage of the C-O bond allows the loss of the good leaving group, a neutral water molecule, to give a carbocation intermediate. This is the rate determining step (bond breaking is endothermic) |
|
| Step 3: An acid/base reaction. Deprotonation by a base (a water molecule) from a C atom adjacent to the carbocation center leads to the creation of the C=C |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |