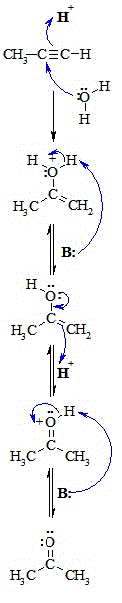
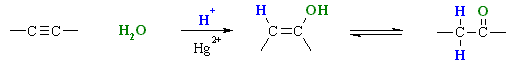Step 1:
Simultaneous acid / base reaction and reaction with the nucleophile.
Protonation of the alkyne (the π electrons act pairs as a Lewis base) with Attack of the nucleophilic water molecule on the electrophilic carbocation
creates an oxonium ion.
Step 2:
An acid / base reaction. Deprotonation by a base generates the alcohol
and regenerates the acid catalyst forming an unstable enol.
Step 3:
An acid / base reaction. Reprotonation by the acid catalyst occurs on
the carbon. The oxygen atom electrons help facilitate this process generating
an oxonium ion.
Step 4:
Another acid / base reaction. Deprotonation of the oxonium ion creates
the ketone. Steps 4 and 5 show the acid catalysed tautomerisation of the
enol to the ketone. |