| Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions |
| Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions |
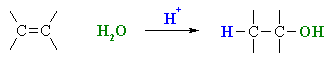
Summary
| MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALKENES WITH H3O+ | |
| Step 1: An acid / base reaction. Protonation of the alkene to generate the more stable carbocation. The pi electrons act as a Lewis base. |
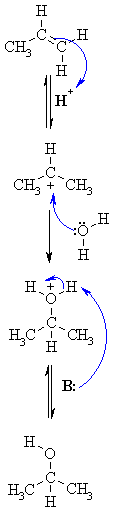 |
| Step 2: Attack of the nucleophilic water molecule on the electrophilic carbocation creates an oxonium ion. |
|
| Step 3: An acid / base reaction. Deprotonation by a base generates the alcohol and regenerates the acid catalyst. |
|
| In this scheme, examples of what the B: could be inlcude the conjugate base of the acid catalyst (e.g. HSO4-), the C=C in the starting material or a molecule of H2O. | |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |