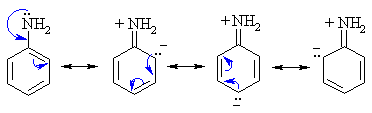 |
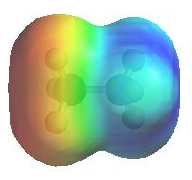
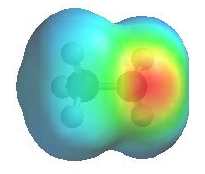
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for methylamine, CH3NH2. The more red
an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue
an area is, the lower the electron density.
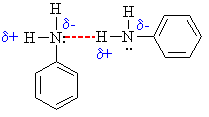
- The amine N atom is a
region of high electron density (red)
due to the lone pair.
- Amine N atoms are Lewis
bases, (alkyl ammonium pKa ~ 10, aryl ammonium pKa ~ 5)
- Amines can react as either
bases or nucleophiles at the nitrogen.
- There is low electron
density (blue) on H atom of the
-NH group.
- Removal of the proton
generates the amide ion
(care : not to be confused with the carboxylic acid derivative
RCONH2)
- The -NH group is a very
poor leaving group and needs to be converted to a better leaving group
before substitution can occur.
|