| Chapter 9 : Alkynes |
| Chapter 9 : Alkynes |
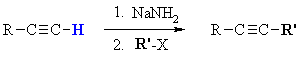
Summary
| MECHANISM FOR ALKYLATION OF ALKYNES | |
| Step 1: An acid / base reaction. The amide ion acts as a base removing the acidic terminal H to generate the acetylide ion, a carbon nucleophile. |
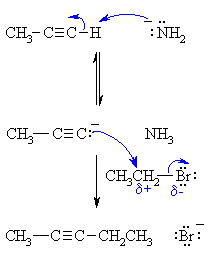 |
| Step 2: A nucleophilic substitution reaction. The carbanion reacts with the electrophilic carbon in the alkyl halide with loss of the leaving group, forming a new C-C bond. |
|
| What is the product of the reactions of CH3-C≡C- with each of the following: | |||
| (a) 2-bromopropane | ANSWER | (d) ethanol | ANSWER |
| (b) 1-iodooctane | ANSWER | (e) ethyl tosylate | ANSWER |
| (c) (R)-2-bromohexane | ANSWER | (f) bromobenzene | ANSWER |
Related reactions:
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |