|
|
|
|
Reactivity of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Carboxylic acid derivatives react tend to react via nucleophilic acyl substitution where the group on the acyl unit, R-C=O undergoes substitution:
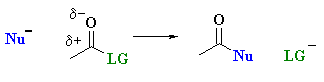
| Study Tip: Note that unlike aldehydes and ketones, this reactivity of carboxylic acids retains the carbonyl group, C=O. . |
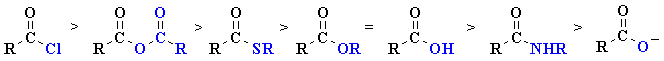
| It is useful to view the carboxylic
acid derivatives as an acyl group, R-C=O, with a different
substituent attached. The important features of the carboxylic acid derivatives that influence their reactivity are governed by this substitutent in the following ways:
|
 |
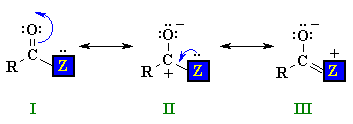 |
I and II are similar to those of aldehydes and ketones, but there is also a third possibility III where a lone pair on the heteroatom Z is able to donate electrons to the adjacent positive center. The stronger this electron donation from Z the less positive the carbonyl C and the less electrophilic the carbonyl group. The ability of Z to donate electrons is linked to its electronegativity...the more electronegative Z is, the less the stabilising effect. |
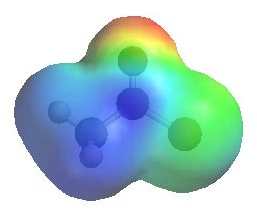
Use the following series of electrostatic potential maps to look at the electrophilicity of the carbonyl C in a example of each the more common carboxylic acid derivatives. Note how the blue colour gradually reduces in intensity down the series.
|
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for ethanoyl chloride. The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density. |
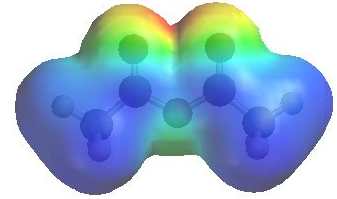 |
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for ethanoic anhydride. The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density. |
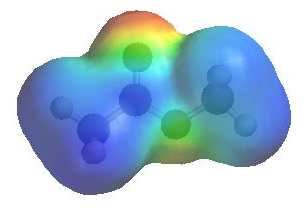
|
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for methyl ethanoate. The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density. |
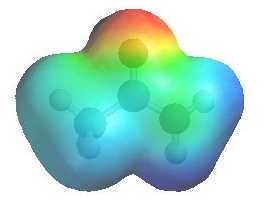
|
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for ethanamide. The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density. |
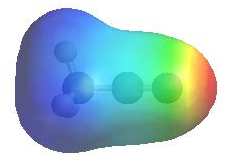
|
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for acetonitrile. The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density. |
| Derivative | Substituent |
|
Leaving Group Ability | Relative Reactivity |
| Acyl chloride | -Cl |
|
|
|
| Anhydride | -OC=OR |
|
|
|
| Thioester | -SR |
|
|
|
| Ester | -OR |
|
|
|
| Acid | -OH |
|
|
|
| Amide | -NH2, -NR2 |
|
|
|
| Carboxylate | -O- |
|
|
|
It is also useful to appreciate where aldehydes and ketones fit into the reactivity scale towards nucleophiles:
acyl halides > anhydrides > aldehydes > ketones > esters = carboxylic acids > amides
QUESTION
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |