| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
Aldehydes and Ketones
| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
Aldehydes and Ketones
Nomenclature:
Aldehydes: functional group suffix = -al (review)
Ketones: functional group suffix = -one (review)
Functional group prefix = oxo-
(Note that an aldehyde is higher priority than a ketone)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
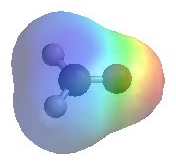 |
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for methanal (formaldehyde) The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density.
|
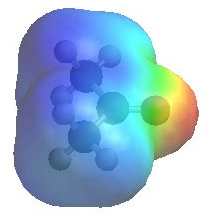 |
The image shows the electrostatic
potential for propanone (acetone). The more red an area is, the higher the electron density and the more blue an area is, the lower the electron density.
|
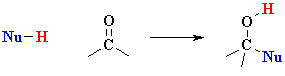
| IMPORTANT : The
reactivity of aldehydes and ketones can be easily rationalised by considering
the important resonance contributor which has a +ve C and -ve O.
Note that this matches the ideas shown in the electrostatic potential diagrams shown above. |
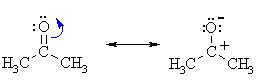 |
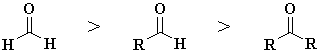
In general the reactivity
order towards nucleophiles is as shown to the right : methanal
> aldehydes
> ketones
|
 |
The images below show spacing filling models so that you can investigate the accessiblity
to the electrophilic C across a series of aldehydes and ketones where the size of the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl C change from -H to t-butyl (-C(CH3)3 ).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |