| Chapter 18: Enols and Enolates |
| Chapter 18: Enols and Enolates |
MECHANISM OF ACID
CATALYSED TAUTOMERISATION |
|
| Step 1: First, an acid-base reaction. The Lewis basic O atom of the carbonyl is protonated by the acid catalyst giving an oxonium ion. |
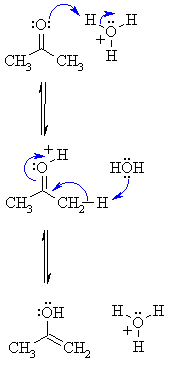 |
| Step 2: Another acid-base reaction. Removal of an α-hydrogen by a water molecule functioning as a base allows formation of the C=C and neutralises the positive charge on the O giving the enol and regenerates the catalyst. |
|
|
|||||||
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |