|
|
|
|
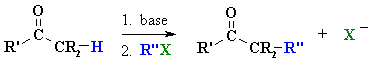
Summary
MECHANISM OF ALKYLATION
OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES |
|
| Step 1: First, an acid-base reaction. Hydroxide functions as a base and removes the acidic α-hydrogen giving the reactive enolate. |
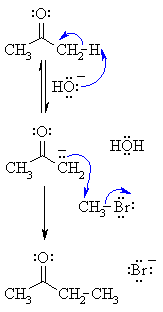 |
| Step 2: The nucleophilic enolate attacks the alkyl halide at the electrophilic carbon carrying the halogen via an SN2 type process giving alkylated ketone and a bromide ion. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |