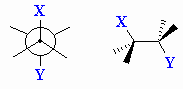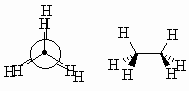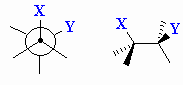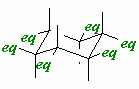|
|
|
| Anti |
Description given to two substitutents attached to
adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 180o with respect to
each other. |
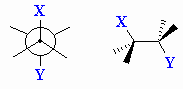 |
| Eclipsed |
A high energy conformation where the bonds on adjacent
atoms are aligned with each other. |
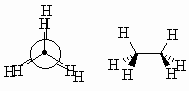 |
| Staggered |
A low energy conformation where the bonds on adjacent
atoms bisect each other, maximising the separation. |
 |
| Gauche |
Description given to two substitutents attached to
adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 60o with respect to
each other. |
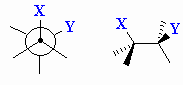 |
| Syn |
Description given to two substitutents attached to
adjacent atoms when their bonds are at 0o with respect to each
other. |
 |
| Conformations |
Different spatial arrangments that a molecule can
adopt due to rotation about sigma bonds. |
|
| Conformers |
Contracted version of conformational isomers. |
|
| Rotamers |
Alternative expression for conformational isomers. |
|
| Conformational
isomers |
Structures that can be interconverted by rotation
about σ bonds. |
|
| Cycloalkane |
An ring containing only C-C bonds. |
|
| Heteroatom |
A non-carbon atom such as O,N,S etc. |
|
| Heterocycle |
A cyclic molecule that includes a heteratom such
as O,N,S etc. as part of the ring. |
|
| Puckered |
A non-planar geometry of a cyclic structure. |
|
| Ring flipping |
The process by which a ring changes it's conformation. |
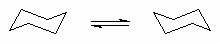 |
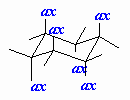
| Axial |
A position on a chair cyclohexane in which the bond
to the ring is perpendicular to the average plane of the ring (i.e.
pointing towards the poles). |
 |
| Equatorial |
A position on a chair cyclohexane in which the bond
to the ring is approximately in the average plane of the ring (i.e.
around the equator). |
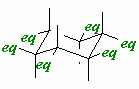 |
| Chair |
The most stable conformation for cyclohexane. |
 |
| Boat |
A high energy conformation of cyclohexane
that occurs during ring flipping. |
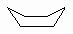 |
| Strain |
Energy associated with a system due to its geometry. |
|
| Angle strain |
Destabilisation due to distortion of a bond angle
from its optimum value caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons
in the bonds. |
 |
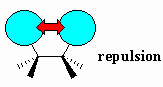
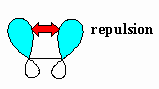
| Van der Waals strain |
Destabilisation due to the repulsion between the
electron clouds of atoms or groups. Also known as Van der Waals repulsion.
This occurs when atoms or groups are too close to each other due to the
electrostatic repulsion of the electrons. |
 |
| Steric strain |
A composite of the other strains (angle, torsional,
Van der Waals) within a molecule. |
|
| Torsional strain |
Destabilisation due to the repulsion between pairs
of bonds caused by the electrostatic repulsion of the electrons in the
bonds. |
 |
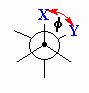
| Torsional angle |
Angle between C-X and C-Y bonds in a X-C-C-Y system
when viewed along the C-C bond. Rotation about the C-C bond will change
this torsional angle. This is also known as a dihedral angle. |
 |
| Ring strain |
The destabilisation of a cyclic structure compared
to a related non-cyclic structure, mainly due to angle and torsional strain.
This extra energy is released when the ring is broken. |
|