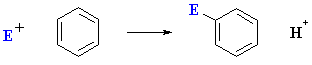 |
Chapter 12 :Reactions of Arenes. Electrophilic Aromatic
Substitution
|
 |
|
Summary
The structure and properties of aromatic systems
were discussed in Chapter 11. Now it
is time to visit their chemical reactions.
The arene system contains an electron rich C=C system which react with
electrophiles via a substitution pathway (to preserve aromaticity) via what
is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution (EArS):
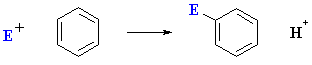
What does the term "electrophilic aromatic substitution" actually imply ?
- An electrophile, E+, is an electron poor species
that will react with an electron rich species (the arene)
- Aromatic because the reaction is characteristic of aromatic systems.
- A substitution implies that a group is replaced (usually H).
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
reactions are the very important class of reactions that allow the introduction
of substituents onto arenes.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
reactions
Problems