Note that no other reagents are needed in order to complete any of these sequences, you should only be using what is there.
Common errors : (1)
(2) not accounting for all bonding changes (3) balancing formal charges
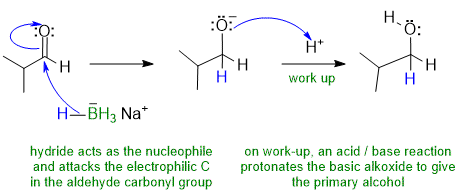
1A Hydride reduction of an aldehyde with NaBH4 to give a primary alcohol : an example of nucleophilic addition:

Common errors : (1) H- as an electrophile; B- as a nucleophile (2) used acidic conditions to protonate carbonyl (3) re-protonation arrows missing/incorrect
1B Hydride reduction of an ester with R2AlH (e.g. "DIBAL") to give an aldehyde: an example of nucleophilic acyl substitution:
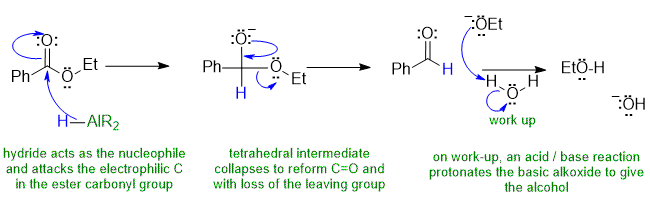
Common errors : (1) H- as an electrophile, Al as a nucleophile (2) the tetrahedral intermediate (2nd structure above) was protonated prior to carbonyl reformation (3) EtOH re-protonation arrows missing/incorrect
2A Intramolecular Freidel-Crafts alyklation:
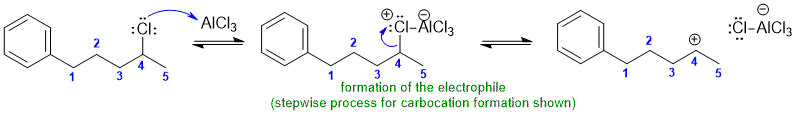
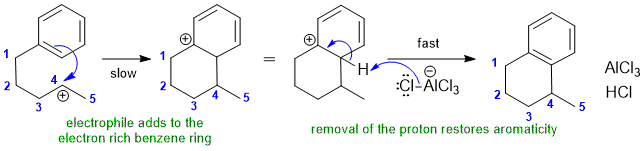
Common errors : (1) spontaneous generation of C+ (2) elimination from C+ (3) missed the electrophilic aromatic substitution reactio (4) incorrect carbocycle ring size (5) incorrect Me position (fix count and label)
2B Esterification of an alcohol with an anhydride (nucleophilic acyl substitution):
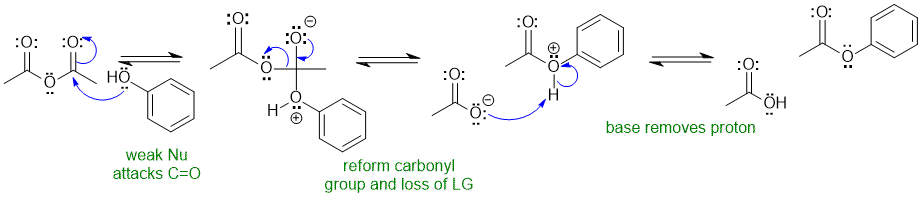
Common errors : (1)