Part 5: MECHANISMS
Note that no other reagents are needed in order to complete any of these sequences, you should only be using what is there.
General common errors:
(1) incorrect formal charges (2) backwards arrows (3) not showing the arrows for all the bonding changes (i.e. missing steps) (4) misuse of resonance / equilibrium arrows (5) vague arrows e.g. not starting where the electrons are i.e. on a bond or lone pair.
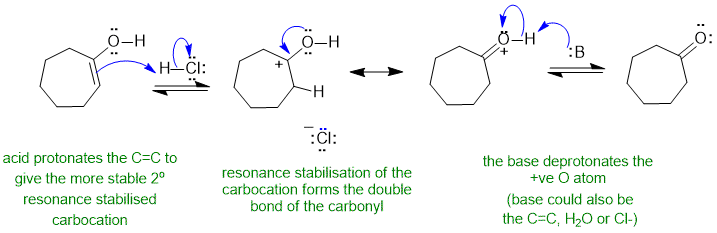
A1 acid catalysed enol to ketone tautomerisation :

Common errors : incorrect use of the resonance arrow, not using the acid to protonate the C=C.
A2 Acid catalysed electrophilic addition of ROH to C=C (like hydration) :
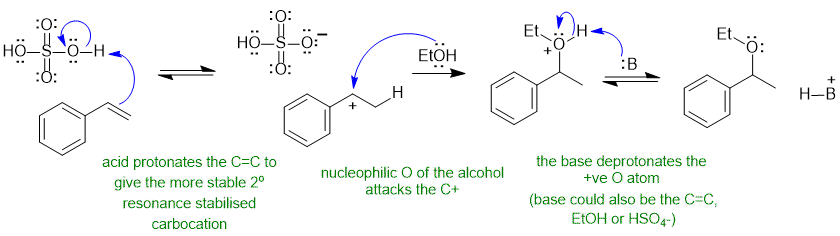
Common errors : using sulfuric acid as a base instead of an acid, deprotonating the alcohol to give the alkoxide despite the acidic conditions
B1 Hydrohalogenation of an alkyne (normal reaction) :
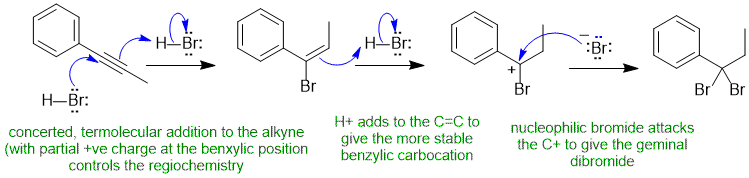
Common errors : drew a mechanism for alkyne via a very unstable vinyl C+ rather than the termolecular concerted path (known based on kinetics and as covered in lecture), not showing the addition to the alkene as stepwise reaction via a stable C+, incorrect product (e.g. tetrabromide) or wrong regiochemistry, confused the HBr reaction with Br2 reaction. Drawing a radical reaction rather than heterolytic mechanism.
B2 Radical hydrohalogenation of an alkyne :
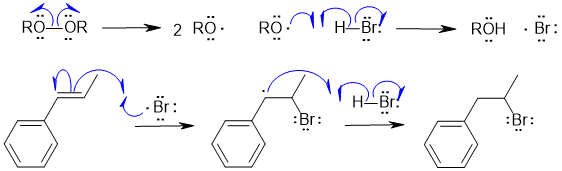
Common errors : not showing a radical reaction, too many radicals forming and combining rather than the radical chain process, incorrect product.