NOTES
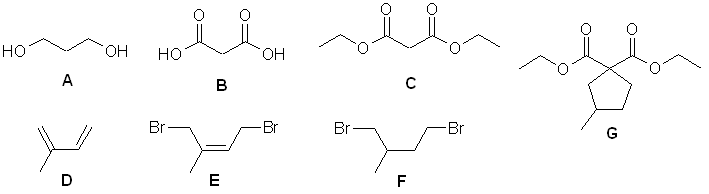
A
elemental analysis gives C3H8O2, IR shows
-OH, 13C implies symmetry
A to B = oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic
acid
B to C = esterification, ethyl ester obtained -
nmr indicates symmetrical diethyl ester
D C5H8 IHD = 2, IR suggests C=C
and 13 C shows 4 sp2C so it looks like a diene.
D to E = conjugate addition of bromine to give
the dibromide.
E to F = reduction of alkene to alkane
C + F to G = form enolate of active methylene and double
alkylation with dibromide F.
G to 3-methylcyclopentanecarboxylic
acid = ester hydrolysis and decarboxylation (gas lost is CO2)
Mechanism : 1,4-conjugate addition of Br2 to a conjugated
diene.
KEY steps.... You should be able to work out A and D from the data provided about each of these compounds.
![[Chem 350 Home]](mol.gif)