Part
5: STRUCTURE DETERMINATION
a. Molecular weight = 6 x 12.01 + 10 x 1.008 + 1 x 16.00 = 98.14 g/mol (1 mark)
b. The formula for index of hydrogen deficiency, IHD = 0.5 ( 2c+2-h), therefore, the IHD = 0.5 (2 x 6 + 2 - 10) = 2 (1.5 marks)
c. Functional groups with 1 x O atom and upto 1 unit of unsaturation : aldehyde, ketone, alcohol, ether, epoxide (1.5 marks)
d. An IR absorption at 1715 cm-1 suggests a ketone. Cyclohexanone is the easiest compound to match the MF with the right number of C and H types. (2 marks)

e.To have the most acidic H being a pKa =25 requires a terminal alkyne. For the most acidic H to be 25, there can't be an alcohol present. (2 marks)
![]()
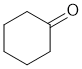
f. For resonance stabilisation, you need a conjugated system (extended pi system). To be Z,Z neither double bond can be at the end of a chain. A few of the possible answers are shown below: (3 marks)
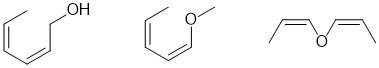
g. A chiral center in this structure will require an sp3 C with 4 different groups attached. A few of the possible answers are show below: (2 marks)
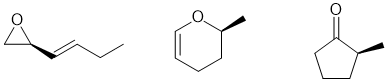
Common errors:
b. Incorrect IHD calculation (but still drew isomers with the right IHD !) : they must be consistent!
c. Naming functional groups with 2 O atoms (the molecular formula had only 1 O).
d. Drawing an aldehyde (incorrect IR frequency).
e
.Drawing internal alkynes instead of terminal alkynes and drawing alkynes with incorrect geometry. They are liner at the alkyne!
f
. Drawing pi bonds with incorrect stereochemistry (carbonyls aren't E or Z).
g
. Not showing the stereochemistry at the chirality center (read the question).