| Chapter 23: Aryl Halides |
Halogenation of Benzene
(review of Chapter 12)

Summary.
- Overall transformation : Ar-H toAr-X
- Reagent : normally the halogen (e.g. Br2) with a Lewis acid catalyst
- The active catalyst is not Fe (0) but the FeX3 formed by reaction of Fe with X2
- Electrophilic species : the halonium ion (i.e. X +) formed by the removal of a halide ion by the Lewis acid catalyst
- Restricted to Cl2 and Br2. I- or F- are usually introduced using alternative methods
|
|
|
| Step 1:
The bromine reacts with the Lewis acid to form a complex that makes the bromine more electrophilic. |
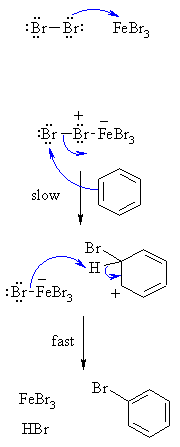 |
| Step 2:
The π electrons of the aromatic C=C act as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic Br, and displacing iron tetrabromide. This step destroys the aromaticity giving the cyclohexadienyl cation intermediate. |
|
| Step 3:
Removal of the proton from the sp3 C bearing the bromo- group reforms the C=C and the aromatic system, generating HBr and regenerating the active catalyst. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |