| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
| Chapter 21: Ester Enolates |
In Chapter 18 we introduced the enolates of aldehydes and ketones (review) and looked at their reactions as C nucleophiles (review). These enolates were formed by treating the aldehyde or ketone with a suitable base :
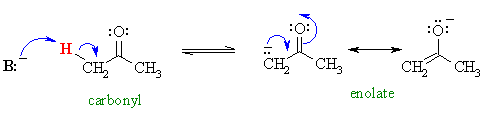
Now we will investigate another group of carbonyl containing compounds, the esters, which behave in a very similar fashion.....
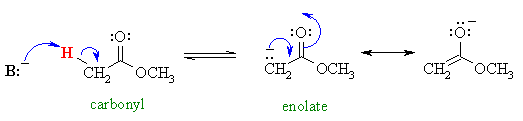
This avoids problems caused by transesterification (conversion of one ester into another)......
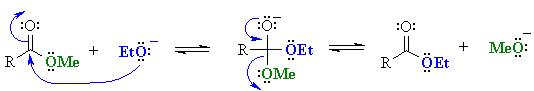
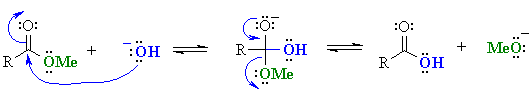
Note that in both cases the problem arises because the base reacts as a "nucleophile"
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |