| Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution |
| Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution |
Reduction of Nitriles
(for more detail see Chapter 22)
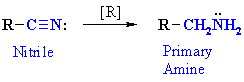
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Addition
Summary
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |