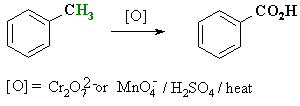|
Chapter 19:
Carboxylic Acids
|
 |
Oxidation of Alkyl Benzenes
(review of Chapter 11)
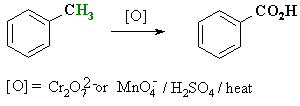 Reaction type: Oxidation
Reaction type: Oxidation
Summary:
- When treated under strong oxidising
conditions, benzylic-H are oxidised all the way to the carboxylic acid.
- Common reagents : Hot, acidic
KMnO4
- The alkyl substituent can be
methyl-, 1o or 2o alkyl.
- 3o alkyl are not
oxidised because they lack a benzylic-H.
- Simple alkane C-H can not be
oxidised in this manner.
- This, therefore gives a potential
route to aromatic carboxylic acids.
QUESTION
Why don't 3o alkyl aromatic substituents get oxidised ? ANSWER