|
|
|
|
![]()
Reaction type : Nucleophilic Addition
Summary
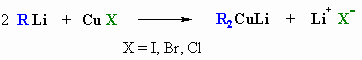
STUDY TIPS:
|
Related reactions
|
|
|
| Step 1: The nucleophilic C in the cuprate attacks the conjugated ketone at the electrophilic alkene C in a nucleophilic addition type process with the electrons being pushed through to the electronegative O, giving an intermediate enolate. |
 |
| Step 2: On acidic work-up, the enolate is protonated at the α-C creating the more favourable carbonyl group. |
|
|
* This is a simplified representation of the mechanism |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |