| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
Oxidation of Aldehydes
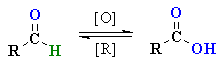
Summary
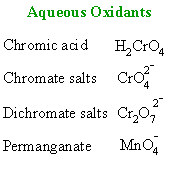
| OXIDATION
OF ALDEHYDES |
|
| Part 1: Formation of the hydrate (mechanism) occurs first. |

|
| Part 2: Now we essentially have an alcohol which reacts with the chromium species to form a chromate ester. |
|
| Part 3:
A base (here a water molecule) abstracts a proton from the chromate ester, the C=O forms and a Cr species leaves. This is really an E2 elimination reaction. Note the importance of the original aldehyde H... if its' missing, no oxidation can occur. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |