| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
Reactions of Secondary Amine Derivatives
 |
| enamine |
Summary
NUCLEOPHILIC
ADDITION OF A SECONDARY AMINE GIVING AN ENAMINE |
|
Step 1: |
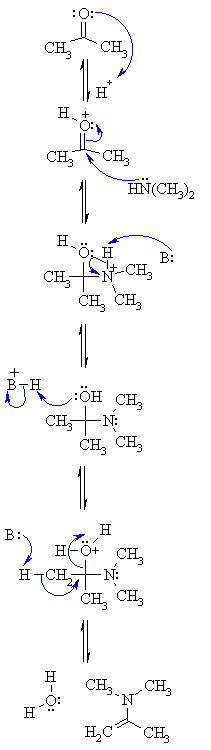 |
| Step 2: Attack of the N nucleophile at the electrophilic C of the C=O group with the electrons from the π bond going to the +ve O. |
|
| Step 3: An acid/base reaction. Removal of the proton neutralises the +ve charge on the N and forms the carbinolamine intermediate. |
|
| Step 4: To form the enamine we need to dehydrate. However, before -OH leaves it needs to be protonated, so a simple acid/base reaction. |
|
| Step 5: Removal of a proton from an adjacent C allows the C=C π bond to form and loss of the leaving group, a neutral water molecule, creating the enamine. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |