| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
Hydroboration / Oxidation
of Alkenes
(review of Chapter 6)
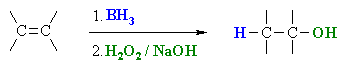
Summary.
| MECHANISM
FOR REACTION OF ALKENES WITH BH3 |
|
| Step 1:
A concerted reaction. The p electrons act as the nucleophile with the electrophilic B and the H is transferred to the C with syn stereochemistry. |
 |
| Step 2:
First step repeats twice more so that all of the B-H bonds react with C=C |
|
| Step 3:
Peroxide ion reacts as the nucleophile with the electrophilic B atom. |
|
| Step 4:
Migration of C-B bond to form a C-O bond and displace hydroxide. Stereochemistry at the C center is unchanged i.e. it is retained. |
|
| Step 5:
Attack of hydroxide as a nucleophile with the electrophilic B displacing the alkoxide. |
|
| Step 6: An acid / base reaction to form the alcohol. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |