| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
Mass Spectroscopy (MS)
What should you be able to do with MS ?
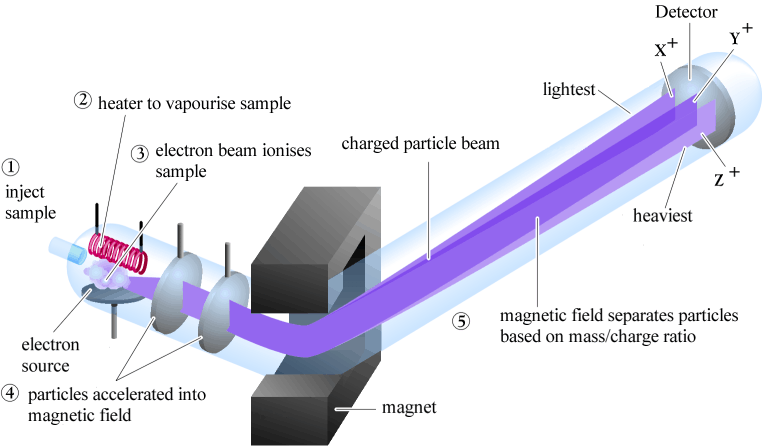
| Mass spectrometry is based on slightly different principles than the other
spectroscopic methods.
The physics behind mass spectrometry is that a charged particle passing
through a magnetic field is deflected on a circular path with a radius
that is proportional to the mass to charge ratio, m/e so for +1 ions, the radius of the path is proportional to the mass of the molecule (i.e. the MW). |
 |
| Molecular ion | The ion obtained by the loss of an electron from the molecule |
| Base peak | The most intense peak in the MS, assigned 100% intensity |
| M+ | Symbol often given to the molecular ion |
| Radical cation | +ve charged species (i.e. a cation) with an odd number of electrons (i.e. a radical) |
| Fragment ions | Lighter cations formed by the decomposition of the molecular ion.
These often correspond to stable carbcations. |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |