| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
| Chapter 13: Spectroscopy |
Since spectroscopy is based on the interaction of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with a molecule, an understanding of electromagnetic radiation is a must.
Spectroscopy monitors the changes in energy states of a molecule, so one must be familiar with the important energy states and concept of quantisation of energy within a molecule.
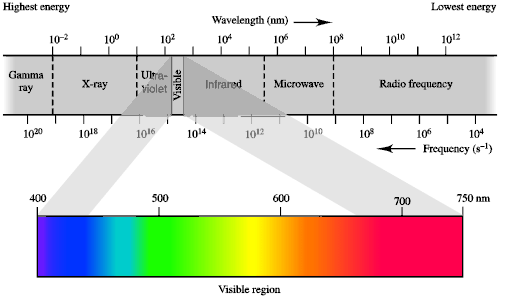
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)The part of the electromagnetic
radiation spectrum that you are most familar with is "visible light" but this
is just a small portion of all the possible types.
QUESTION : Can you think of common applications of
other regions of the electromagnetic spectrum ? ANSWER
Electromagnetic radiation has both particle and wave properties.
QUESTION Can you think of an example of each ? ANSWER
Wave-like properties:Energy States
It is important to understand wavelength, l ,and frequency, n, and how they relate to each other : c = l n
(c = speed of light)Particle-like properties:
A particle of energy is called a photon.
Each photon has a discrete amount of energy : a quantum, E = h n = h c / l
(h = Planck's constant)
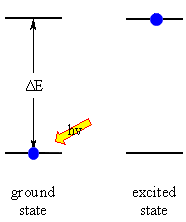 |
The absorption of energy causes an atom or molecule to go from an initial
energy state (the ground state) to another higher energy state (an excited
state). The energy changes are frequently described using an energy
level diagram.
The energy states are said to be quantised because there are only certain
discrete values that are possible, there is not a continuous spread
of energy levels available. |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |