|
|
|
|
Reactions and Reagents
The following table contains a summary of the key
reactions to introduce a substituent onto an aromatic system.
More detailed information on each reaction can be accessed by following the
link from the reaction column.
Reactions that can be used to convert existing aromatic substituents are listed
separately.
Study Tips:
|
|
|
|
Electrophile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
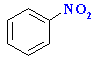
|
E+ formed by loss of water from nitric acid |
|
|
H2SO4 or SO3 / H2SO4 |
|
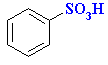 |
Reversible (heat with aq. acid) |
| Halogenation |
|
|
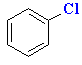
|
E+ formed by Lewis acid removing Cl- |
|
|
|
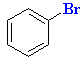
|
E+ formed by Lewis acid removing Br- | |
|
|
|
|
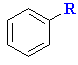
|
E+ formed by Lewis acid removing Cl- |
|
|
|

|
E+ formed by loss of water from alcohol | |
|
|
|

|
E+ formed by protonation of alkene | |
|
|
|
|
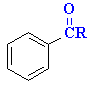
|
E+ formed by Lewis acid removing Cl- |
|
|
|

|
E+ formed by Lewis acid removing RCO2- |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |