| Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions |
| Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions |
Ozonolysis of Alkenes
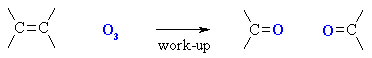
Summary
|
||||
![how to visualise ozonolysis with [R] work-up](C=CtoC=O.gif)
|
![how to visualise ozonolysis with [O] work-up](C=CtoCOOH.gif)
|
|||
QUESTION
|
||||
|
(a) ethene ? |
ANSWER ANSWER |
(c) cis
or trans-2-butene ? (d) 2-methylpropene ? |
ANSWER ANSWER |
|
| MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALKENE OZONOLYSIS | |
| Step 1: The π electrons act as the nucleophile, attacking the ozone at the electrophilic terminal O. A second C-O is formed by the nucleophilic O attacking the other end of the C=C. |
 |
| Step 2: The cyclic species called the malozonide rearranges to the ozonide. |
|
| Step 3: The ozonide decomposes on work-up. Reductive work-up with (usually Zn / acetic acid) gives the two carbonyl groups. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |