 |
|
 |
|
| Nomenclature |
Formula |
3D structure |
| Functional class name = alkyl alcohol e.g. ethyl alcohol Substituent suffix = -ol e.g. ethanol Substituent prefix = hydroxy- e.g. hydroxyethane Structural unit : alcohols contain R-OH |
|
|
ethanol |
CH3CH2OH |
|
propan-2-ol or 2-propanol
(or isopropanol) |
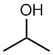 CH3CH(OH)CH3 |
|
but-3-en-1-ol or 3-buten-1-ol
|
CH2=CHCH2CH2OH |
|
| ©Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |