 |
Chapter 20: Carboxylic
Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution |
 |
Interconversion Reactions
of Esters
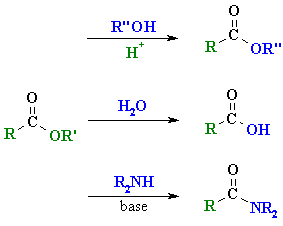 |
esters |
| acids |
| amides |
Reaction type: Nucleophilic
Acyl Substitution
Summary
- Esters can be converted into other
esters (transesterification), the parent carboxylic acid (hydrolysis) or amides
(see above).
- Transesterification :
heat with alcohol and acid catalyst
- Hydrolysis
: heat with aq. acid o base (e.g. aq. H2SO4
or aq. NaOH) (see next page for more details)
- Amide preparation :
heat with the amine, methyl or ethyl esters are the most reactive
