|
|
|
|
Basic α-Halogenation of Aldehydes and Ketones

Summary
|
|
|
| Step 1:
First, an acid-base reaction. Hydroxide functions as a base and removes the acidic α-hydrogen giving the enolate. |
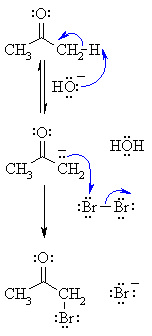 |
| Step 2:
The nucleophilic enolate reacts with the halide giving the halogenated ketone and a bromide ion. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |