| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
| Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones. Nucleophilic Addition to C=O |
Oxidation of Primary
and Secondary Alcohols
(review of Chapter 15)
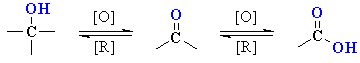
Summary
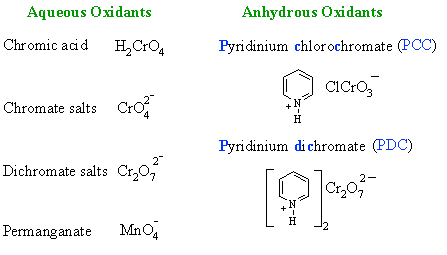
| Study Tip: If you see Cr reagents, you are probably looking at an oxidation reaction of a alcohol or an aldehyde. |
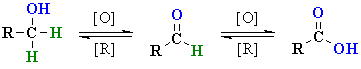 |
| 1o alcohol aldehyde |
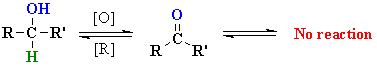 |
| 2o alcohol ketone |
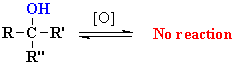 |
| 3o alcohol |
Cr OXIDATION OF ALCOHOLS |
|
| The mechanism is not trivial,
so attention here is focussed on the actual oxidation step. Prior to this,
the alcohol reacts to form a chromate ester (shown). A base (here
a water molecule) abstracts a proton from the chromate ester, the C=O forms and a Cr species leaves. This demonstrates the importance of the carbinol H to this mechanism. |
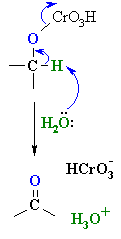 |
QUESTIONS
| ANSWER | ||
|
|
ANSWER | |
|
|
ANSWER | |
| ANSWER |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |