| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
| Chapter 15: Alcohols, Diols and Thiols |
Synthesis of Ethers via Acid-catalysed Condensation of Alcohols
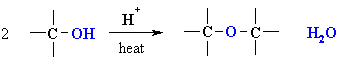
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Substitution (SN2)
Summary
Related reactions
|
|
|
| Step 1:
An acid/base reaction. Protonation of the alcoholic oxygen to make a better leaving group. This step is very fast and reversible. The lone pairs on the oxygen make it a Lewis base. |
 |
| Step 2: The O of the second alcohol molecule functions as the nucleophile and attacks to displace the good leaving group, a neutral water molecule, by cleaving the C-O bond. This creates an oxonium ion intermediate. |
|
| Step 3: Another acid / base reaction. The proton is removed by a suitable base (here a water molecule, ROH is another alternative) to give the ether product. |
|
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |