| Chapter 10: Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems |
| Chapter 10: Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems |
Radical Halogenation of Allylic systems
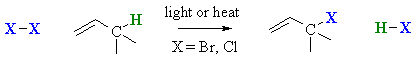
Summary
| RADICAL CHAIN MECHANISM FOR
ALLYLIC BROMINATION |
|
| Step 1 (Initiation) Heat or uv light causes the weak halogen bond to undergo homolytic cleavage to generate two bromine radicals and starting the chain process. |
 |
| Step 2 (Propagation) (a) A bromine radical abstracts a hydrogen to form HBr and an allyl radical, then (b) The allyl radical abstracts a bromine atom from another molecule of Br2 to form the allyl bromide product and another bromine radical, which can then itself undergo reaction 2(a) creating a cycle that can repeat. |
 |
| Step 3 (Termination) Various reactions between the possible pairs of radicals allow for the formation of Br2 or the product, allyl bromide. These reactions remove radicals and do not perpetuate the cycle. |
 |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |