| Chapter 4: Alcohols and Alkyl Halides |
| Chapter 4: Alcohols and Alkyl Halides |
Reaction of Alcohols with other Halogenating agents (SOCl2,PX3)
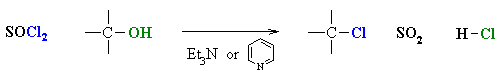
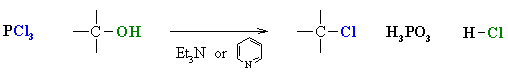
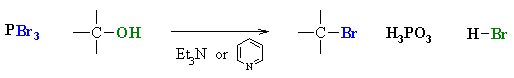
Reaction type: Nucleophilic Substitution (usually SN2)
Summary
| SN2 MECHANISM FOR REACTION OF ALCOHOLS
WITH SOCl2 |
|
| Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4: |
 |
| © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |