| Chapter 5: Pushing Curly Arrows |
| Chapter 5: Pushing Curly Arrows |
Key Issues :
In the early stages of learning to use curly arrows it may be
helpful to use Lewis structures to help you see those all important electrons.
Note that the mechanisms throughout this website are drawn showing lone
pairs, especially those on oxygen and nitrogen because they are important.
Bond Breaking :
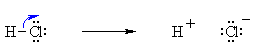
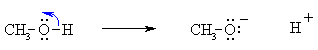 Do the charges balance ? Yes, in both cases we have a neutral molecule going to +ve and -ve ions whose charges cancel. Now an example of resonance where a π-bond is broken, again the curly arrow starts at the bond and ends on an atom:
Do the charges balance ? Yes, we have a neutral molecule going to give a +ve and -ve which cancel. Bond Making Processes:
Do the charges balance ? Yes, in each case +ve and -ve combine to give a neutral molecule. In the 2nd and 3rd cases, because a bond already existed, we increased the bond order and created multiple bonds. |
 |
© Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |