| Chapter 1: Structure Determines Properties |
| Chapter 1: Structure Determines Properties |
Knowing the formal charge on a particular
atom in a structure is an important
part of keeping track of the electrons and is important for
establishing
and predicting the reactivity.
The formal charge on an atom in a molecule reflects the electron count associated with the atom compared to the isolated neutral atom. If the atom has given away electrons it will be +ve and if it has gained electrons it will be -ve.
Although formal charge can be calculated via a mathematical formula, or a diagram, it is also possible to do it "instinctively" based on comparing structures. The "instinctive method" is quicker, and is probably what your instructor uses, but it does require more skill and an experience of common structures.
Formal charge equation formally compares the number of valence electrons in an isolated neutral atom (which can be determined from the older style group number of the periodic table) with the number of valence electons around the atom in the molecule:
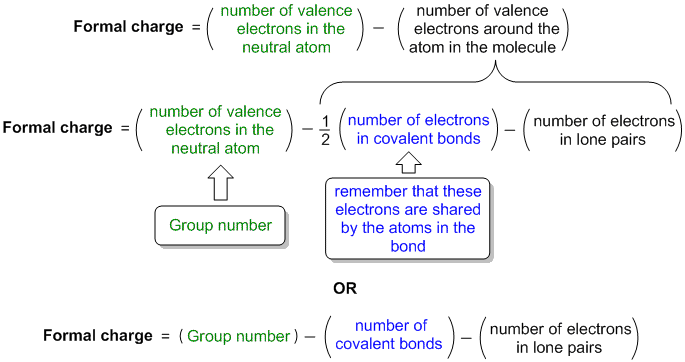
Diagramatic or visual method visually compares the number of valence electrons in an isolated neutral atom (which can be determined from the older style group number of the periodic table) with the atom in the molecule. It's a visual equivalent of the equation based mthod described above.
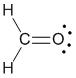 |
Example molecule of interest |
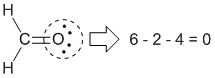 |
Formal charge on oxygen: Group number = 6 |
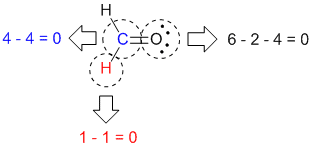 |
Formal charges for all the different atoms |
Instinctive
method
This is based on comparing the structure with common, known neutral
structures. To do this you need to recognise the common neutral
structures:
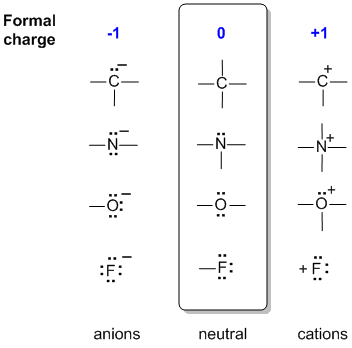
C 4 bonds, N 3 bonds, 1 lone pair, O 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs, F 1 bond, 3
lone pairs. Notice how these numbers work in relation to the octet rule (4 pairs). Once mastered, this is much quicker.
In the middle of the following diagram are the neutral bonding situations for C, N, O and a halogen, F. (For example, just think of each central atom as being bonded to hydrogen atoms).
To the left, a bond has been lost but converted to a lone pair, so the central atom has gained an electron and become -ve.
To the right, there are 2 scenarios:
 |
Now would be a good time to check out some questions
 |
© Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry, University of Calgary |  |