| Chapter 1: Where are the Electrons? |  |
| Chapter 1: Where are the Electrons? |  |
Atoms
1. How many electrons are there in each of the following : N- , O2-, F- and C+ ?
N has 7 electrons so N- has 7+1 = 8, 6 valence and 2 core
O has 8 electrons so O2- has 8+2 = 10, 8 valence and 2 core
F has 9 electrons so F- has 9+1 = 10, 8 valence and 2 core
C has 6 electrons so C+ has 6-1 = 5, 3 valence and 2 core
2. What is the atomic mass unit for an atom of bromine?
79.904 amu, which is the weighted average of the isotopic masses for 79Br (50.7%) and 81Br (49.3%).
3. How many protons and neutrons are there is each of the following : 1H, 2H, 12C, 16O, 35Cl and 37Cl ?
The atomic number, Z, which defines the number of protons is defined by the elemental symbol. The mass numbers are given as superscripts before the atomic symbol. Note that because atoms are neutral, the number of positive protons also defines the number of negative electrons surrounding the nucleus.
| Element | Atomic number | Mass number | Protons | Neutrons |
| 1H | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2H | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 12C | 6 | 12 | 6 | 6 |
| 16O | 8 | 16 | 8 | 8 |
| 35Cl | 17 | 35 | 17 | 18 |
| 37Cl | 17 | 37 | 17 | 20 |
1. Which quantum number defines an orbitals energy level for (a) the hydrogen atom and (b) other atoms ?
2. What are the quantum numbers that describe a 3p orbital?(a) For the hydrogen atom, the principle quantum number, n, defines the energy level.
(b) For atoms other than hydrogen atom, the principle quantum number, n, and the angular momentum quantum number, l, define the orbital energy levels.
First determine what quantum numbers are indicated by the name 3p.
3. How many occupied valence orbitals are there in Cl and I?Any of the following 'sets' of quantum numbers will be valid:
n l ml 3 1 1 3 1 0 3 1 -1
First consider their electron configurations (core, valence)4. What are the quantum numbers for an electron in a 3s orbital?
Both have a total of four, occupied, valence orbitals, one s orbital and three p orbitals.
First determine what quantum numbers are indicated by the name 3s.Electron Configurations
Then note that you want the quantum numbers for an electron so ms must also be considered!
Any of the following 'sets' of quantum numbers are valid.
n l ml ms 3 0 0 -1/2 3 0 0 +1/2
Use the information given in the box below when answering
the next three questions:
| (a) [Ar] | (d) 1s22s22p63s23px23py1 |
| (b) 1s22s22p63s1 | (e) 1s22s22p63s23px13py13pz1 |
| (c) 1s22s22p63p1 |
1. Which of the electron configurations above best
describes the ground state electron configuration of Cl-? (a)
2. Which of the electron configurations above is possible for the ground
state of P? (e)
3. Which of the electron configurations above describes an excited state
of Mg+? (c)
4. Is the following electron configuration consistent with Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity?
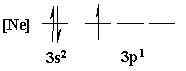
Yes, all electrons unpaired before pairing
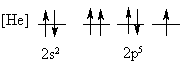
No, two electrons in a p orbital have the same four quantum numbers
7. What is the orbital energy diagram that best describes the valence electron configuration of O ?
Did you draw the core or did you draw the valence electron configuration by mistake ?
Did you draw the valence or did you draw the core electron configuration by mistake ?