Part 9: SYNTHESIS
The schemes below give possible syntheses of the targets. There
are of course other variations. The first part for each compound gives a "retro-synthesis",
the "plan" and then the required forward synthesis with reagents is
given. Red arrows try to show carbon-carbon bond forming reactions, blue arrows
are functional group manipulations. The blue text rationalise the retrosynthetic
analysis and information about important reactions are given in green.
Quick and simple suggestions for analysis / solutions for now.....images take a while to draw.....

1. Cyclohexane derivative with defined
stereochemistry.... Diels-Alder (actually very similar to number 2)
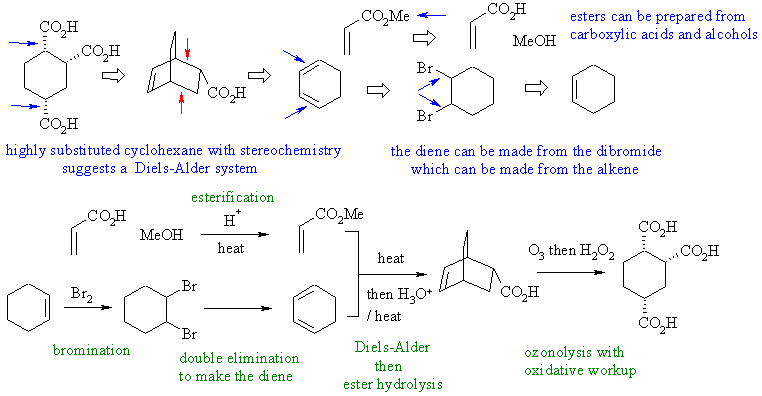
2.
Cyclohexane derivative with defined stereochemistry....
Diels-Alder.
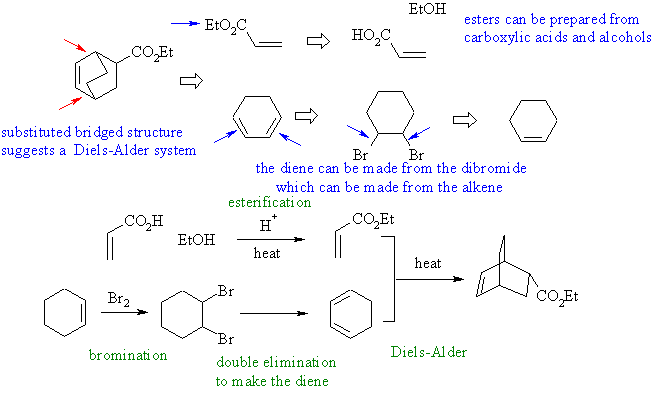
3. An
ether with aromatic rings. The ether could come from a Williamson
ether synthesis of the primary -OH and primary -Br
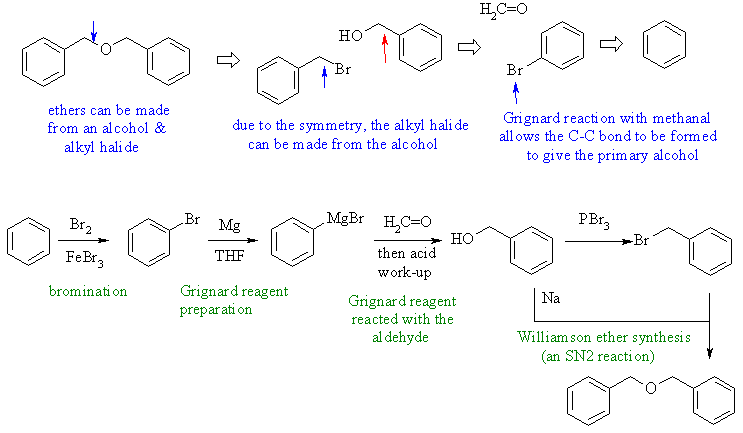
4.
Alpha aryl cyclohexanone (enolate will not work since Ar-Br don't do
SN1 or SN2), therefore get ketone via oxidation of secondary alcohol

5.
Beta-hydroxy carbonyl = enolate chemistry.... here a Claisen of an
ester - reduction of ketone to -OH needed as well
- The propanoate ester (CH3CH2-CO2Et) can be made from the acid and
an alcohol : CH3CH3-CO2H + EtOH + H+ / heat
- Claisen.... CH3CH2-CO2Et plus NaOEt gives the beta-keto ester
: CH3CH2C(=O)CH(CH3)COOEt
- Reduce the ketone with NaBH4 to leave ester unreacted to give the
product, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH(CH3)COOEt
6. A
para-nitro ether..... ether suggests using a Williamson ether
synthesis. So use the alkyl bromide and the p-nitrophenol - the
phenol can be made via diazonium chemistry
- Benzene to nitrobenzene to aminobenzene to diazobenzene to
phenol....C6H6 -- HNO3/H2SO4 -> C6H5NO2 -- Sn / HCl then NaHCO3
--> C6H5NH2 -- NaNO2 / HCl --> C6H5N2+ -- H2O / H2SO4 /
heat --> C6H5OH
- Phenol to p-nitrophenol C6H5OH -- HNO3/H2SO4 ->
HOC6H4NO2
- p-nitrophenol to p-propoxynitrobenzene : HOC6H4NO2 +
CH3CH2CH2Br + K2CO3 (base) --> CH3CH2CH2OC6H4NO2
7. A
1,3,5-trisubstituted aromatic.... 2 acid groups.
- Benzoic acid.... C6H5Br + Mg / THF -> C6H5MgBr
then add CO2 (work up with H3O+) give C6H5CO2H (benzoic acid)
- Nitrate using HNO3/H2SO4 to give m-nitrobenzoic acid
- Reduce and the diazotise using Sn/HCl then Na2CO3, then NaNO2/ HCl
- Use CuCN to get the nitrile, then hydrolyse the nitrile with H3O+ / heat to give the meta-dicarboxylic acid.
- Now use FeBr3 / Br2 to get the bromine m to the 2 acid groups.
8.
Tertiary alcohol, 2 aryl groups the same suggests Grignard chemistry of
an ester... ester from carboxylic acid + alcohol
- Benzoic acid.... C6H5Br + Mg / THF -> C6H5MgBr
then add CO2 (work up with H3O+) give C6H5CO2H (benzoic acid)
- Benzoate ester....C6H5CO2H + EtOH / H+ / heat ---> C6H5CO2Et
- p-bromotoluene....C6H6 + CH3Cl + AlCl3 --> C6H5CH3 ---
Br2 / FeBr3 --> p-CH3C6H4Br
- Grignard ....p-CH3C6H4Br + Mg / THF -> CH3C6H4MgBr
- Add 2 eq. Grignard to ester : 2 CH3C6H4MgBr +
C6H5CO2Et --(work up with H3O+)--> target





