Part 6: THERMODYNAMICS
This should have been a reasonably straight forward calculation, but care needs to be taken with the last part of the question.
a. C5H12 + 8 O2 --> 5 CO2 + 6 H2O (1 mark)
b. DHc elements = (5 x -94.05) + (6 x -68.32) = -880.17 kcal/mol (0.5 marks)
DHf X= -880.17 - (- 840.03) = -40.14 kcal/mol (0.5 marks)
DHc Y = -880.17 - (- 36.73) = -843.44 kcal/mol (0.5 marks)
c. (1.5 marks)

d.

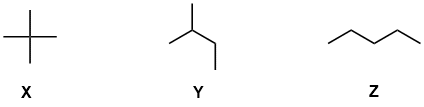
e.Given the thermodynamic data in the table provided in the question, and hence the figure shown above, X is the most stable isomer (i.e. lowest energy) and Z is the least stable isomer (1 mark)
f. The more branched isomer is more stable because branching increases the number of primary C atoms and hence the number of primary C-H bonds. Since, in terms of bond strength, primary C-H bonds > secondary C-H > tertiary C-H, a molecule with more primary C-H (more branching) is more stable (1 mark)
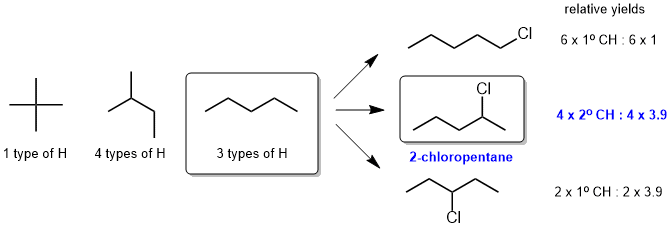
g. Since the radical chlorination reaction gives 3 mono-chlorination products, the starting material must have had 3 types of H and hence the starting material is pentane, isomer Z (X has 1 type and Y has 4 types). The major product of mono-chlorination of pentane is 2-chloropentane (which we can confirm by considering the relative yields based on the terms from the equation that predicts the yields of these reactions.
Common errors: