 |
|
 |
|
|
Formula
|
3D structure
|
|
|
Benzene Benzene is an important structure. It's the most common aromatic hydrocarbon. Since benzene (and its relatives) have their own characteristic reactions,
they are a functional group, often referrred to as arenes |
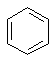
C6H6 |
|
ethylbenzene
|
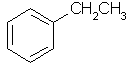 C6H5CH2CH3 |
bromobenzene
|
 C6H5Br |
ethoxybenzene
|
 C6H5OCH2CH3 |
nitrobenzene
|
 C6H5NO2 |
| ©Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |