 |
|
 |
|
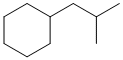
Consider the following examples:
First work out the name of the complex substituent
- this is shown in bold in the figure:
Complex substituent name : 2-methylpropyl
|
 |
|
Now work on the whole structure:
(2-methylpropyl)cyclohexane |
 |
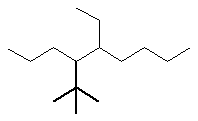
First work out the name of the complex substituent
- this is shown in bold in the figure:
Complex substituent name : 1,1-dimethylethyl
|
 |
|
Now work on the whole structure:
4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-ethylnonane
|
 |
| Alkyl group, R-
|
Common name
|
Complex name (if different) |
| CH3- |
methyl |
|
| CH3CH2- | ethyl |
|
| CH3CH2CH2- | propyl |
|
| (CH3)2CH- | isopropyl |
(1-methylethyl) |
| CH3CH2CH2CH2- | butyl |
|
| CH3CH2CHCH3 | sec-butyl
or s-butyl |
(1-methylpropyl) |
| (CH3)2CHCH2- | isobutyl |
(2-methylpropyl) |
| (CH3)3C- | tert-butyl
or t-butyl |
(1,1-dimethylethyl) |
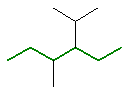
3-ethyl-2,4-dimethylhexane
|
 or  |
| ©Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry |